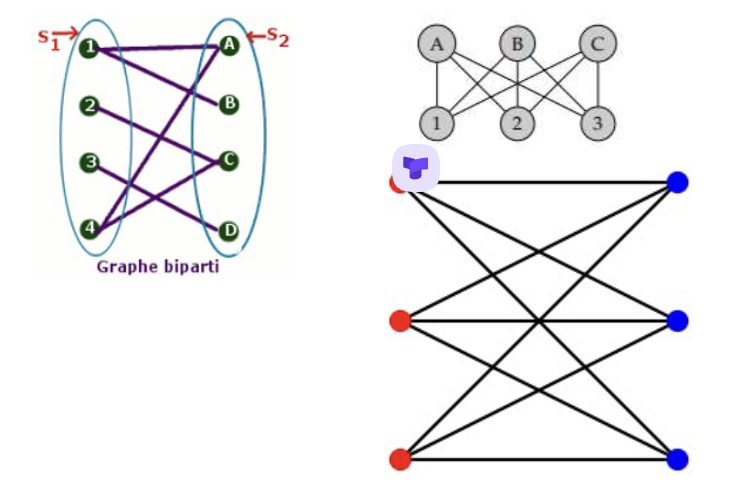
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
| #include "bipartition.h"
int main() {
int n = 10;
MatAdj ma;
ma.nbSom = n;
ma.mat = (int **)malloc(n * sizeof(int *));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
ma.mat[i] = (int *)malloc(n * sizeof(int));
}
int adj[10][10] = {
{0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0}
};
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
ma.mat[i][j] = adj[i][j];
}
}
int *marquage=Marquage(ma);
for (int i=0;i<10;i++) {
printf("%d ",marquage[i]);
}
printf("\n");
Ensemble s1,s2;
s1=initE();
s2=initE();
partition(n,marquage,&s1,&s2);
while (s1!=NULL){
printf("%d ",s1->elt+1);
s1=s1->suiv;
}
printf("\n");
while (s2!=NULL){
printf("%d ",s2->elt+1);
s2=s2->suiv;
}
printf("\n");
if (estBiparti(ma)) {
printf("le graphe est biparti\n");
}else {
printf("le graphe n'est pas biparti\n");
}
}
|